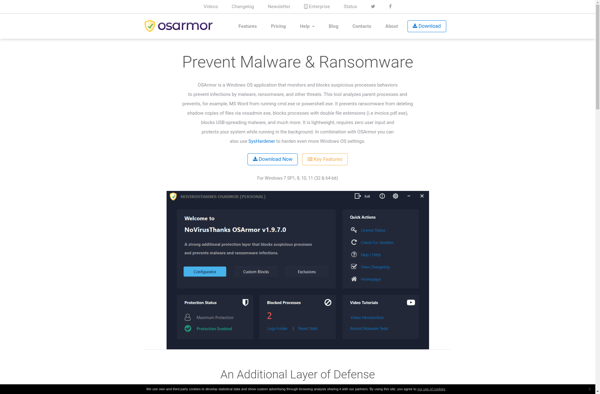
Description: OSArmor is an antivirus and anti-malware software for Windows designed to provide real-time protection against viruses, malware, spyware, ransomware, and phishing attacks. It uses signatures and heuristics to detect threats and includes features like customizable scans, active process monitoring, and web filtering.
Type: Open Source Test Automation Framework
Founded: 2011
Primary Use: Mobile app testing automation
Supported Platforms: iOS, Android, Windows
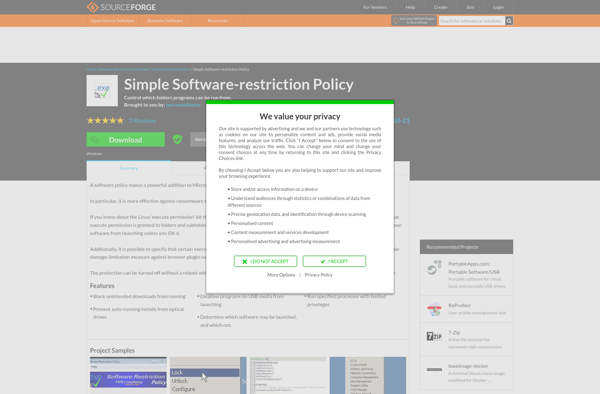
Description: Simple Software Restriction Policy is a feature in Windows that allows administrators to control what software users can run. It works by specifying rules that allow or block software by attributes like file path, hash, or certificate.
Type: Cloud-based Test Automation Platform
Founded: 2015
Primary Use: Web, mobile, and API testing
Supported Platforms: Web, iOS, Android, API