Description: Panda-Sql is an open-source SQL query builder and database management tool for Python. It allows you to write, visualize, and execute SQL code in Python without needing to know SQL syntax.
Type: Open Source Test Automation Framework
Founded: 2011
Primary Use: Mobile app testing automation
Supported Platforms: iOS, Android, Windows
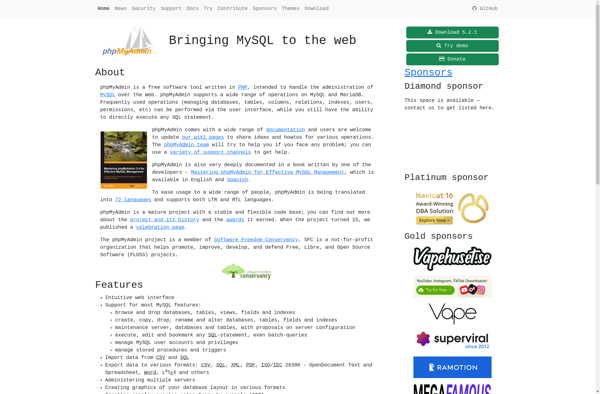
Description: phpMyAdmin is a free and open source administration tool for MySQL and MariaDB. It allows users to manage databases, tables, columns, relations, indexes, users, permissions, and more through a web interface.
Type: Cloud-based Test Automation Platform
Founded: 2015
Primary Use: Web, mobile, and API testing
Supported Platforms: Web, iOS, Android, API