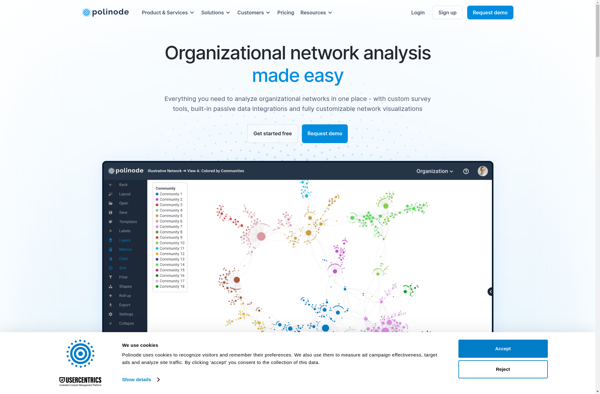
Description: Polinode is an open-source platform for building, training and deploying machine learning models. It provides a visual interface and integrates with popular frameworks like PyTorch and TensorFlow.
Type: Open Source Test Automation Framework
Founded: 2011
Primary Use: Mobile app testing automation
Supported Platforms: iOS, Android, Windows
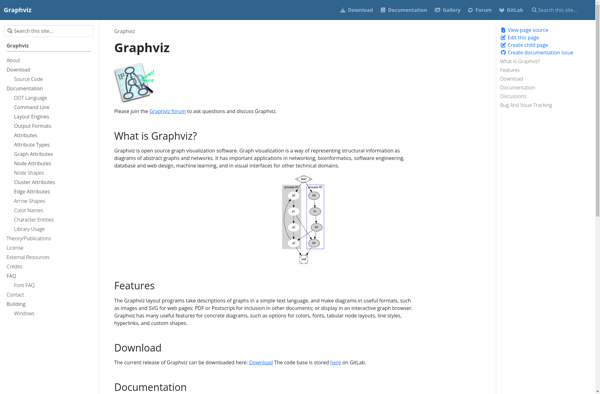
Description: Graphviz is an open source graph visualization software used for representing structural information as diagrams of abstract graphs and networks. It provides useful features for creating a variety of graph types like directed graphs, undirected graphs, hierarchies, and more.
Type: Cloud-based Test Automation Platform
Founded: 2015
Primary Use: Web, mobile, and API testing
Supported Platforms: Web, iOS, Android, API