Description: Radeon ProRender is a powerful physically-based rendering engine that enables creative professionals to produce stunningly photorealistic images on the GPU. It's optimized for AMD Radeon graphics cards.
Type: Open Source Test Automation Framework
Founded: 2011
Primary Use: Mobile app testing automation
Supported Platforms: iOS, Android, Windows
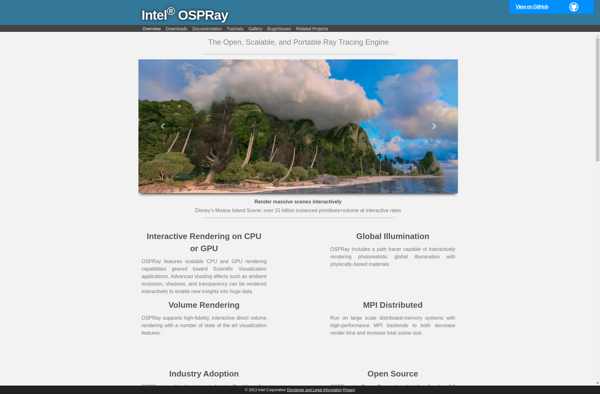
Description: OSPRay is an open-source, scalable, and portable ray tracing engine for high-performance, high-fidelity visualization. It is designed for large visualization applications and aims to be an alternative to hardware-accelerated ray tracers.
Type: Cloud-based Test Automation Platform
Founded: 2015
Primary Use: Web, mobile, and API testing
Supported Platforms: Web, iOS, Android, API