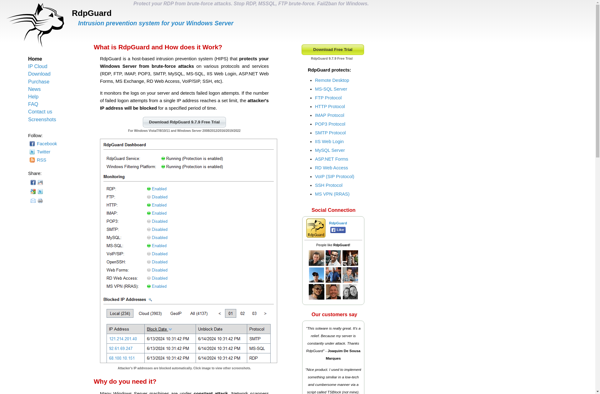
Description: RdpGuard is a remote desktop protection software designed to secure RDP connections against brute force attacks. It includes features like IP blacklisting, account lockouts, advanced authentication protocols, and real-time attack visualization.
Type: Open Source Test Automation Framework
Founded: 2011
Primary Use: Mobile app testing automation
Supported Platforms: iOS, Android, Windows
Description: DenyHosts is an open-source program designed to help system administrators thwart SSH server attacks by blocking IP addresses using failed authentication attempts to detect attackers. It adds IP addresses to the system's /etc/hosts.deny file when it identifies too many failed SSH attempts.
Type: Cloud-based Test Automation Platform
Founded: 2015
Primary Use: Web, mobile, and API testing
Supported Platforms: Web, iOS, Android, API