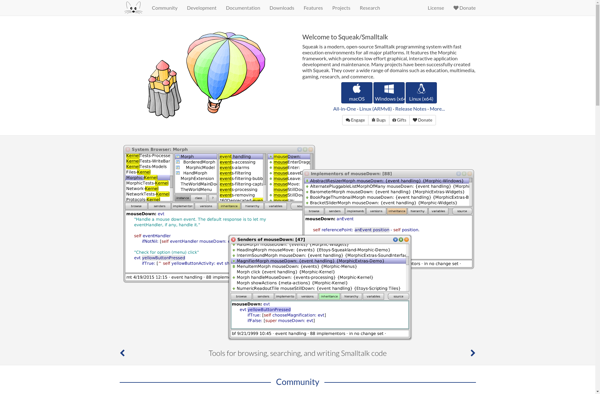
Description: Smalltalk is an object-oriented, dynamically typed, reflective programming language. It was designed for incremental code development and testing, featuring an integrated development environment, a file system, and a system command shell. It paved the way for many IDE features that are now common in other languages.
Type: Open Source Test Automation Framework
Founded: 2011
Primary Use: Mobile app testing automation
Supported Platforms: iOS, Android, Windows
Description: Haskell is a statically typed, purely functional programming language known for its strong static type system, sophisticated type inference, and non-strict evaluation. It is used in education, academia, and some commercial applications.
Type: Cloud-based Test Automation Platform
Founded: 2015
Primary Use: Web, mobile, and API testing
Supported Platforms: Web, iOS, Android, API