Description: Spearmint is an open-source Bayesian optimization software for machine learning. It allows users to optimize hyperparameters and neural network architectures efficiently through Bayesian optimization.
Type: Open Source Test Automation Framework
Founded: 2011
Primary Use: Mobile app testing automation
Supported Platforms: iOS, Android, Windows
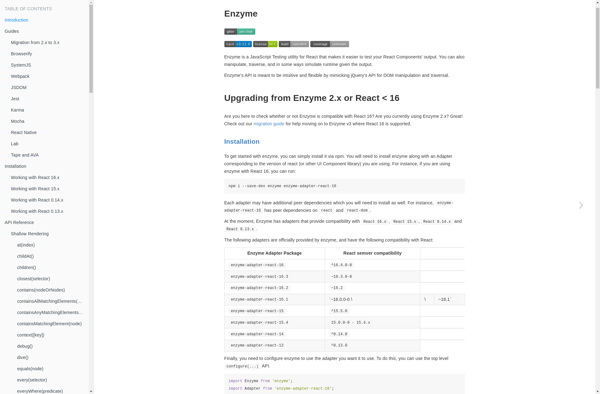
Description: Enzyme is an open-source JavaScript testing utility for React that makes it easier to test React components. It provides capabilities to shallow render component trees, find, manipulate components, and traverse the component tree.
Type: Cloud-based Test Automation Platform
Founded: 2015
Primary Use: Web, mobile, and API testing
Supported Platforms: Web, iOS, Android, API