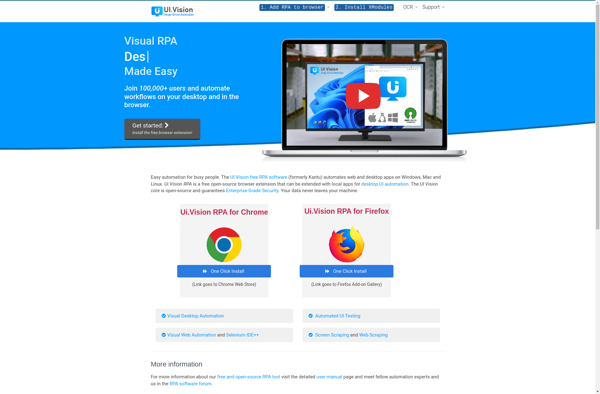
Description: UI.Vision RPA is a robotic process automation (RPA) software that helps automate repetitive tasks. It provides user interface automation to integrate legacy systems and automate workflows.
Type: Open Source Test Automation Framework
Founded: 2011
Primary Use: Mobile app testing automation
Supported Platforms: iOS, Android, Windows
Description: pywinauto is an open source Python library for automating desktop GUI applications on Windows. It allows you to control and interact with windows and controls programmatically, useful for GUI testing and automation.
Type: Cloud-based Test Automation Platform
Founded: 2015
Primary Use: Web, mobile, and API testing
Supported Platforms: Web, iOS, Android, API