Description: UIkit is an open-source web framework for developing fast and powerful web interfaces. It provides a collection of HTML, CSS, and JS components to build responsive, mobile-first websites and apps.
Type: Open Source Test Automation Framework
Founded: 2011
Primary Use: Mobile app testing automation
Supported Platforms: iOS, Android, Windows
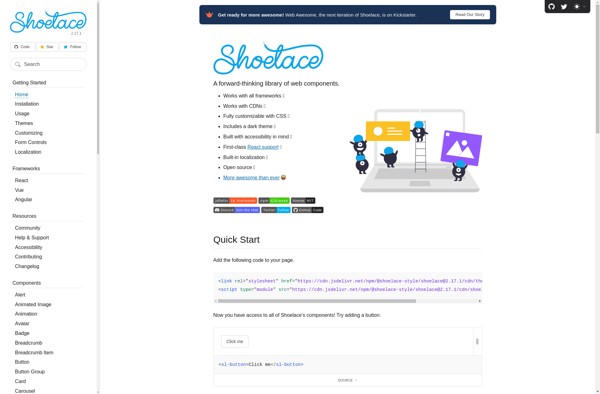
Description: Shoelace.css is an open-source CSS framework that provides pre-designed CSS classes to help developers quickly build responsive web interfaces. It's lightweight and customizable.
Type: Cloud-based Test Automation Platform
Founded: 2015
Primary Use: Web, mobile, and API testing
Supported Platforms: Web, iOS, Android, API