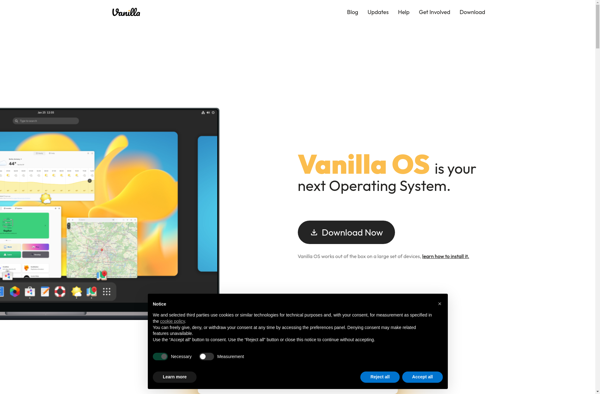
Description: Vanilla OS is a lightweight open-source operating system based on Linux. It focuses on simplicity, efficiency, and ease of use rather than features. Ideal for reviving old hardware or using on low-powered devices.
Type: Open Source Test Automation Framework
Founded: 2011
Primary Use: Mobile app testing automation
Supported Platforms: iOS, Android, Windows
Description: Windows 7 is a personal computer operating system that was produced by Microsoft as part of the Windows NT family of operating systems. It was released to manufacturing in July 2009 and became generally available in October 2009. Windows 7 has improved desktop search, support for touchscreen displays, and home networking improvements over its predecessor, Windows Vista.
Type: Cloud-based Test Automation Platform
Founded: 2015
Primary Use: Web, mobile, and API testing
Supported Platforms: Web, iOS, Android, API