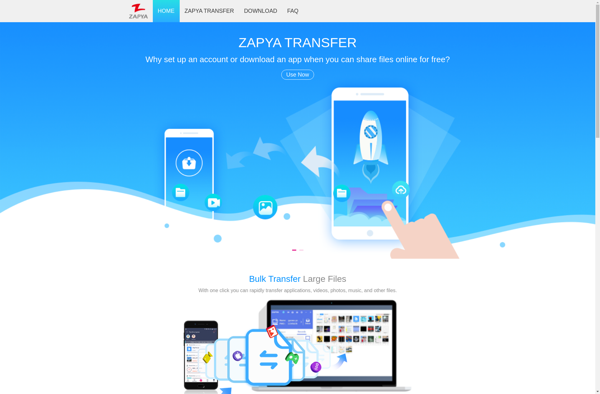
Description: Zapya is a free file sharing app that allows you to transfer files and share content with others nearby without an internet connection. It uses Wi-Fi or Bluetooth to send documents, photos, videos, and other media between devices.
Type: Open Source Test Automation Framework
Founded: 2011
Primary Use: Mobile app testing automation
Supported Platforms: iOS, Android, Windows
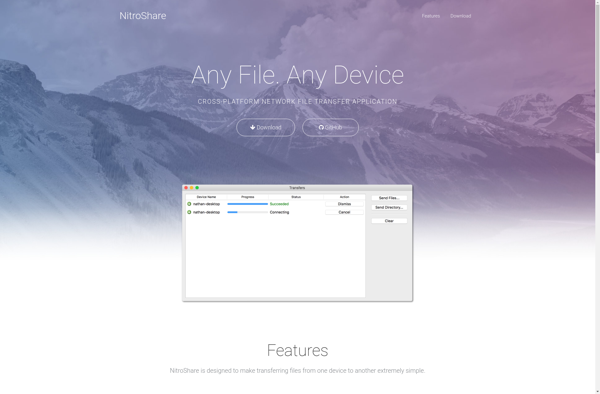
Description: NitroShare is a free and open source program for local network file sharing. It allows users on the same network to easily and securely transfer files between devices running Windows, Mac, or Linux.
Type: Cloud-based Test Automation Platform
Founded: 2015
Primary Use: Web, mobile, and API testing
Supported Platforms: Web, iOS, Android, API