Symbian
Symbian: Discontinued Mobile Operating System
Discover the history and features of Symbian, a pioneering mobile OS that dominated Nokia smartphones in the early 2000s, but ultimately lost ground to iOS and Android.
What is Symbian?
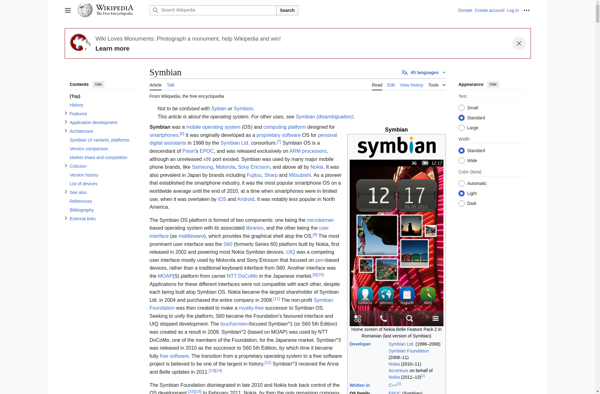
Symbian was a mobile operating system and computing platform designed for smartphones. It was originally developed as a proprietary software OS for PDAs in 1998 by the Symbian company. The Symbian OS and platform were then licensed by phone manufacturers like Nokia.
During the early 2000s, Symbian OS was the most popular smartphone operating system globally, powering many Nokia smartphones and phones from other manufacturers. It offered multitasking and a degree of user interface personalization. However, over time it struggled to keep pace with emerging mobile operating systems like iOS and Android that were quicker to innovate and offered a more user-friendly experience.
The popularity of Symbian OS declined in the late 2000s with the growing market share of iOS and Android smartphones. In 2010, Nokia announced it would replace Symbian with Windows Phone as its primary smartphone OS. Symbian was eventually discontinued altogether as a smartphone platform in 2013.
While Symbian OS was an early pioneer in advanced mobile operating systems for phones, it failed to adapt quickly enough to compete with more modern, user-friendly alternatives like iOS and Android. It lost relevance and market share in the late 2000s, eventually becoming discontinued altogether by 2013 as Nokia and other manufacturers moved on to other OS options for their phones.
Symbian Features
Features
- Microkernel architecture
- Multitasking
- Support for wireless technologies like Bluetooth and IrDA
- Web browsing capabilities
- Messaging and PIM functionality
- Media playback support
- Touchscreen support
- Support for apps and games
Pricing
- One-time Purchase
- Custom Pricing
Pros
Cons
Official Links
Reviews & Ratings
Login to ReviewThe Best Symbian Alternatives
Top Mobile Operating Systems and Discontinued and other similar apps like Symbian
Android
Sailfish OS
Tizen OS

KaiOS
