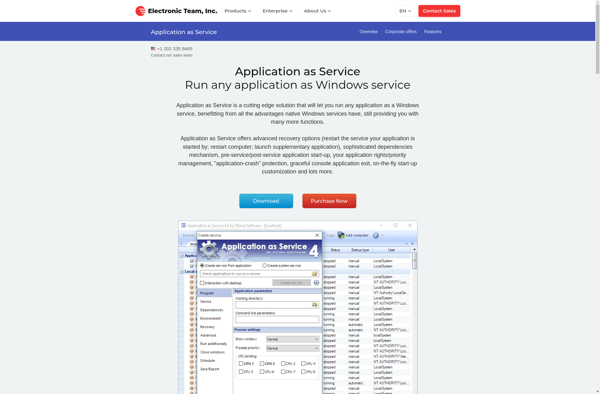
Description: Application as a Service (AaaS) refers to cloud-based software applications that are hosted and managed remotely by a third-party provider and accessed by users over the internet. AaaS delivers applications to users on demand without requiring installation or maintenance.
Type: Open Source Test Automation Framework
Founded: 2011
Primary Use: Mobile app testing automation
Supported Platforms: iOS, Android, Windows
Description: Daemon Master is a software tool for managing and monitoring daemon processes on Linux servers. It provides a graphical interface to start, stop, and configure various daemons, as well as monitor their status and resource usage in real time.
Type: Cloud-based Test Automation Platform
Founded: 2015
Primary Use: Web, mobile, and API testing
Supported Platforms: Web, iOS, Android, API