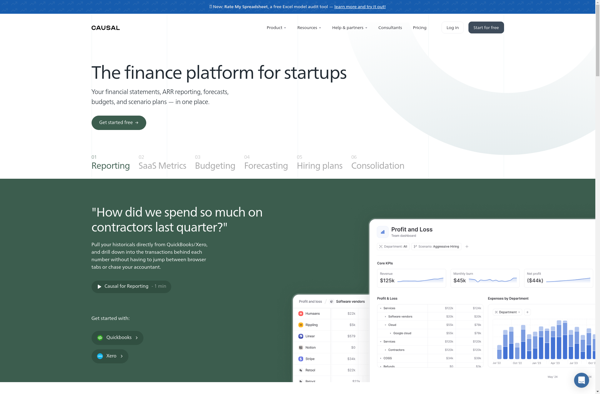
Description: Causal is a no-code platform that enables anyone to analyze the core drivers of business metrics using statistical methods. It makes causal data analysis accessible with an easy-to-use interface to upload data, run analyses, and get clear, actionable insights.
Type: Open Source Test Automation Framework
Founded: 2011
Primary Use: Mobile app testing automation
Supported Platforms: iOS, Android, Windows
Description: Tableau is a popular business intelligence and data visualization software. It allows users to connect to data, create interactive dashboards and reports, and share insights with others. Tableau makes it easy for anyone to work with data, without needing coding skills.
Type: Cloud-based Test Automation Platform
Founded: 2015
Primary Use: Web, mobile, and API testing
Supported Platforms: Web, iOS, Android, API