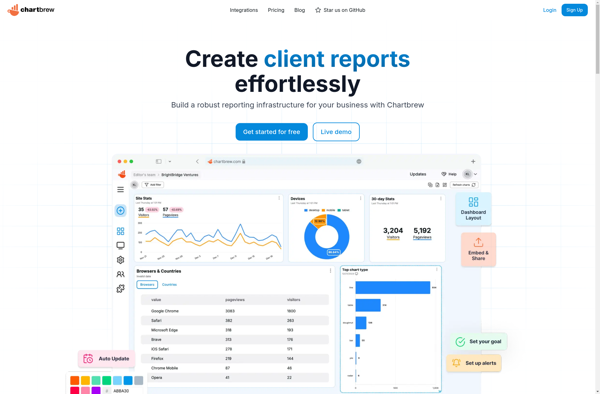
Description: Chartbrew is an open-source business intelligence and data visualization software. It allows users to connect to data sources, build interactive charts and dashboards, and share analytics. Chartbrew is lightweight, customizable, and integrates with popular databases.
Type: Open Source Test Automation Framework
Founded: 2011
Primary Use: Mobile app testing automation
Supported Platforms: iOS, Android, Windows
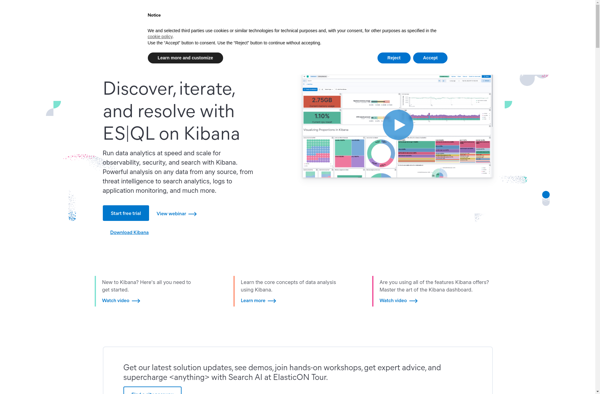
Description: Kibana is an open-source data visualization dashboard for Elasticsearch. It provides visualization capabilities on top of the content indexed on an Elasticsearch cluster. Users can create bar, line and scatter plots, or pie charts and maps on top of large volumes of data.
Type: Cloud-based Test Automation Platform
Founded: 2015
Primary Use: Web, mobile, and API testing
Supported Platforms: Web, iOS, Android, API