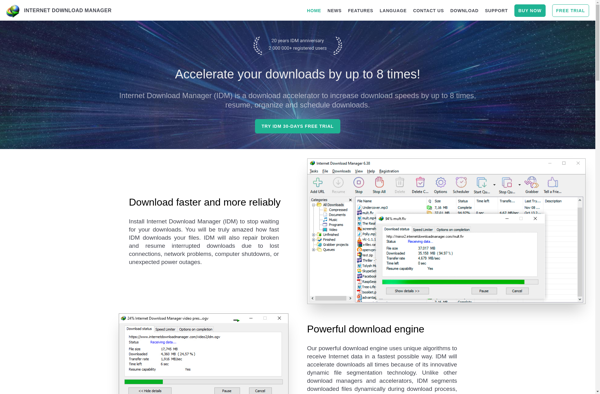
Description: The IDM Integration Module is an add-on for web browsers that integrates with Internet Download Manager. It allows users to easily download files, videos, and more with one click using IDM's advanced download capabilities.
Type: Open Source Test Automation Framework
Founded: 2011
Primary Use: Mobile app testing automation
Supported Platforms: iOS, Android, Windows
Description: Fritz!Load is a free open source load testing tool for web applications. It allows users to simulate multiple concurrent users accessing a website to test performance under load.
Type: Cloud-based Test Automation Platform
Founded: 2015
Primary Use: Web, mobile, and API testing
Supported Platforms: Web, iOS, Android, API