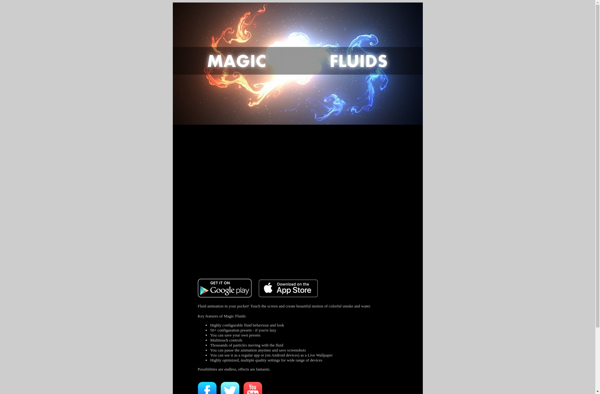
Description: Magic Fluids is a fluid simulation and animation software. It allows users to create realistic liquid, smoke, and other fluid effects for animation and visual effects purposes. The intuitive interface and powerful simulation engine make it easy for both beginners and professionals to achieve high-quality results.
Type: Open Source Test Automation Framework
Founded: 2011
Primary Use: Mobile app testing automation
Supported Platforms: iOS, Android, Windows
Description: HexShaders is a shader editor and shader graph tool for creating shaders in Unity. It allows you to visually create shaders without code using a node-based graph system.
Type: Cloud-based Test Automation Platform
Founded: 2015
Primary Use: Web, mobile, and API testing
Supported Platforms: Web, iOS, Android, API