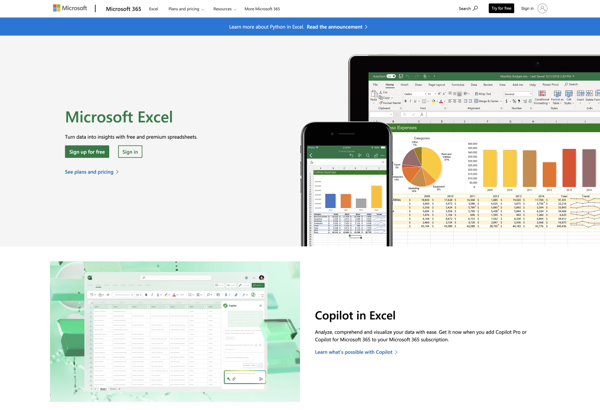
Description: Microsoft Excel, the powerhouse of spreadsheets. Analyze, visualize, and manage data with ease. Create dynamic charts, automate calculations, and make informed decisions using this essential tool for businesses and individuals.
Type: Open Source Test Automation Framework
Founded: 2011
Primary Use: Mobile app testing automation
Supported Platforms: iOS, Android, Windows
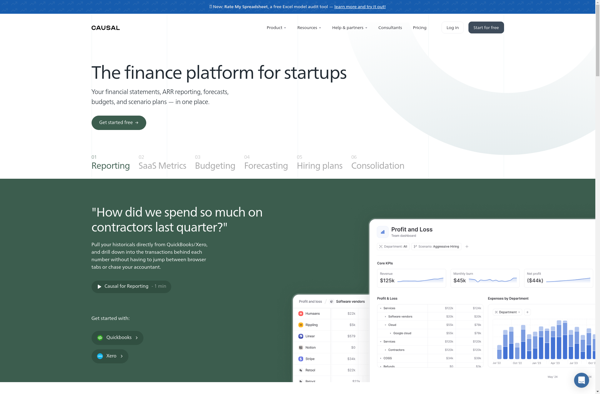
Description: Causal is a no-code platform that enables anyone to analyze the core drivers of business metrics using statistical methods. It makes causal data analysis accessible with an easy-to-use interface to upload data, run analyses, and get clear, actionable insights.
Type: Cloud-based Test Automation Platform
Founded: 2015
Primary Use: Web, mobile, and API testing
Supported Platforms: Web, iOS, Android, API