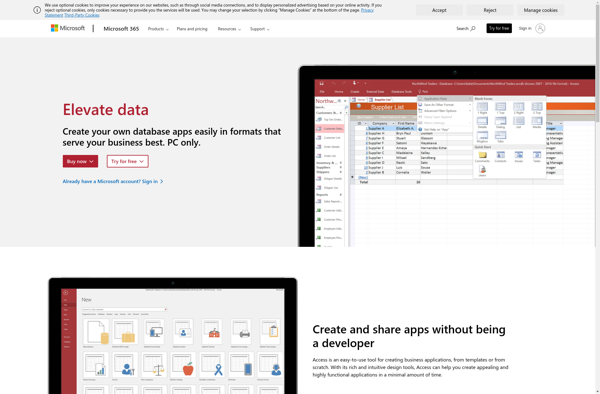
Description: Microsoft Access is a database management system from Microsoft that combines a graphical user interface with a relational database engine. It allows users to create tables, queries, forms, and reports to track and analyze data.
Type: Open Source Test Automation Framework
Founded: 2011
Primary Use: Mobile app testing automation
Supported Platforms: iOS, Android, Windows
Description: LyteRAD is an open-source, lightweight RAD tool for rapid application development. It allows developers to quickly build desktop applications with drag-and-drop widgets and minimal coding.
Type: Cloud-based Test Automation Platform
Founded: 2015
Primary Use: Web, mobile, and API testing
Supported Platforms: Web, iOS, Android, API