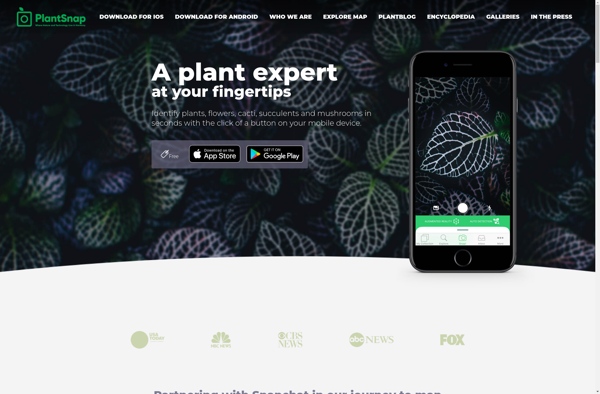
Description: PlantSnap is a mobile app that helps identify plants and flowers. Users can take a photo of a plant using their phone camera and PlantSnap will provide identification results along with information about the plant.
Type: Open Source Test Automation Framework
Founded: 2011
Primary Use: Mobile app testing automation
Supported Platforms: iOS, Android, Windows
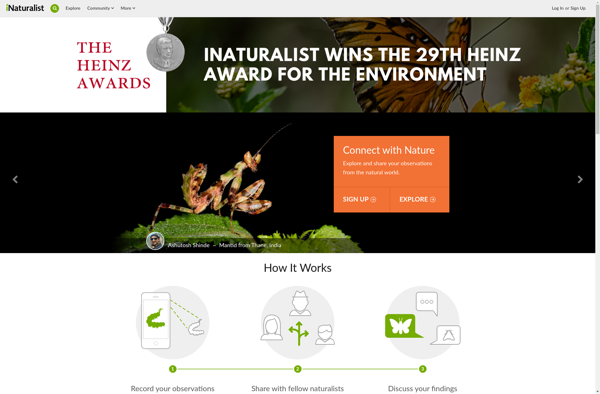
Description: iNaturalist is a citizen science platform that allows users to record and share observations of biodiversity. Users can upload photos and identifications of plants, animals, fungi and other organisms to contribute data for scientific research.
Type: Cloud-based Test Automation Platform
Founded: 2015
Primary Use: Web, mobile, and API testing
Supported Platforms: Web, iOS, Android, API