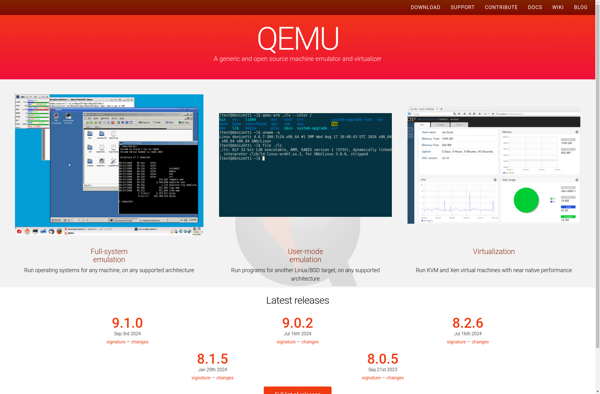
Description: QEMU is an open source machine emulator and virtualizer. It can emulate a complete computer system, including peripherals, and allow you to launch different operating systems without rebooting your physical machine.
Type: Open Source Test Automation Framework
Founded: 2011
Primary Use: Mobile app testing automation
Supported Platforms: iOS, Android, Windows
Description: CoreCluster is an open-source platform for deploying and managing containerized applications across on-prem and cloud environments. It provides a simple yet powerful interface to handle deployment, scaling, networking, security, and more across Kubernetes clusters.
Type: Cloud-based Test Automation Platform
Founded: 2015
Primary Use: Web, mobile, and API testing
Supported Platforms: Web, iOS, Android, API