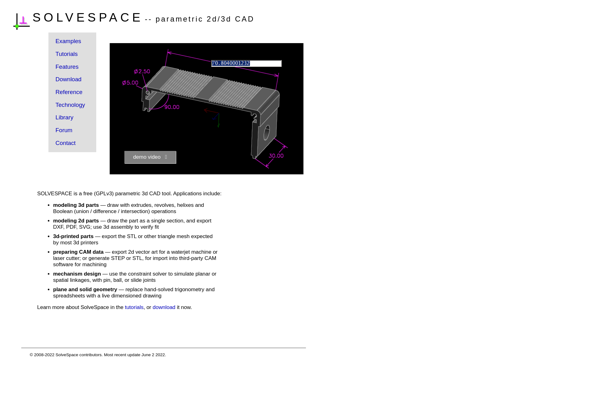
Description: SolveSpace is a free, open source 2D and 3D CAD software for designing and analyzing mechanical designs and assemblies. It has an intuitive user interface with key features like constraint-based sketching, extruding, dimensioning, sectioning, and visualization.
Type: Open Source Test Automation Framework
Founded: 2011
Primary Use: Mobile app testing automation
Supported Platforms: iOS, Android, Windows
Description: OpenSCAD is an open source, free 3D modeling software used for creating solid 3D CAD models. It is script-based and uses a programming language to define the geometry of models rather than an interactive graphical interface.
Type: Cloud-based Test Automation Platform
Founded: 2015
Primary Use: Web, mobile, and API testing
Supported Platforms: Web, iOS, Android, API