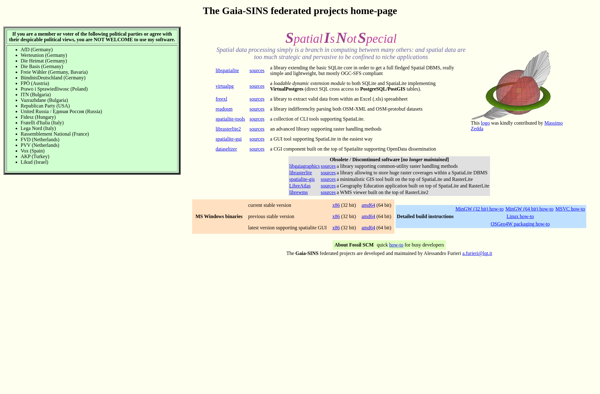
Description: SpatiaLite is an open source spatial database extender for SQLite that adds support for geographic objects and allows SQLite to be used as a full-featured spatial database.
Type: Open Source Test Automation Framework
Founded: 2011
Primary Use: Mobile app testing automation
Supported Platforms: iOS, Android, Windows
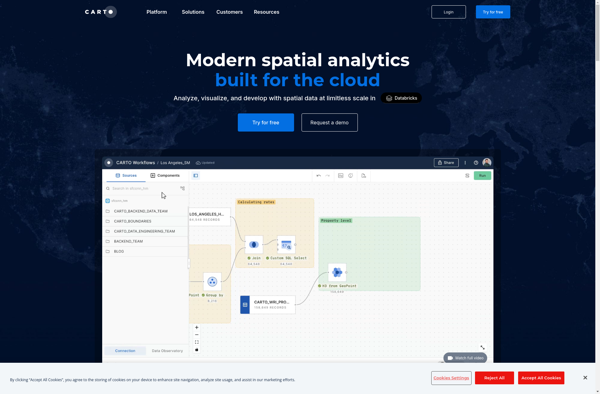
Description: CartoDB is an open source platform for building location intelligence applications. It allows users to visualize geospatial data and perform spatial analysis through an easy to use drag-and-drop interface. Key capabilities include mapping, analysis, and sharing of geospatial data.
Type: Cloud-based Test Automation Platform
Founded: 2015
Primary Use: Web, mobile, and API testing
Supported Platforms: Web, iOS, Android, API