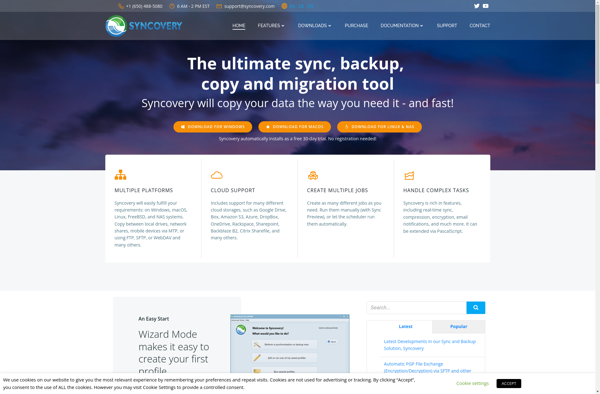
Description: Syncovery is a file synchronization and backup software for Windows, macOS and Linux. It allows easy backing up of data between external drives, network drives, and cloud storage services. Key features include incremental backup, data compression and encryption, scheduling options, and support for many cloud services.
Type: Open Source Test Automation Framework
Founded: 2011
Primary Use: Mobile app testing automation
Supported Platforms: iOS, Android, Windows
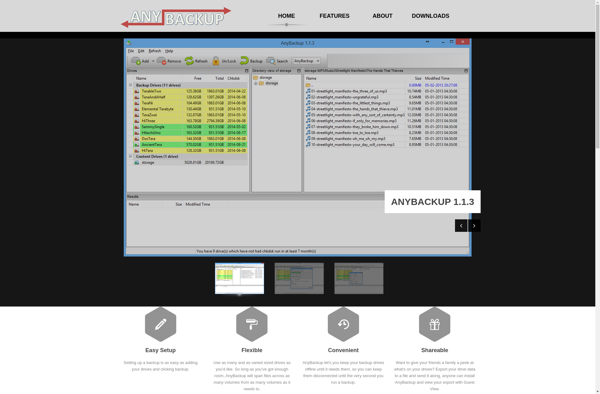
Description: AnyBackup is an easy-to-use backup software for Windows that allows you to backup your files and folders to various storage locations. It provides scheduled and automatic backups, file compression and encryption, and backup to external drives, network locations, FTP, etc.
Type: Cloud-based Test Automation Platform
Founded: 2015
Primary Use: Web, mobile, and API testing
Supported Platforms: Web, iOS, Android, API