Description: SyncTime is a time tracking and productivity software that allows users to track time spent on projects, set goals, generate reports, and synchronize data across devices. It has features for organizing tasks, tracking billable hours, managing teams, and more.
Type: Open Source Test Automation Framework
Founded: 2011
Primary Use: Mobile app testing automation
Supported Platforms: iOS, Android, Windows
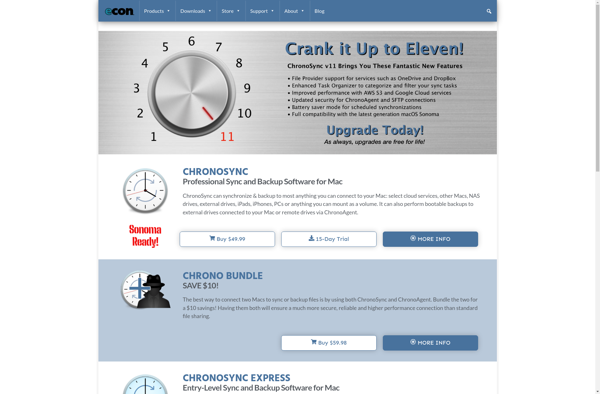
Description: ChronoSync is a file synchronization and backup software for macOS. It allows users to easily sync files between folders, external drives, network volumes, and cloud storage services. Key features include incremental backups, versioning, scheduling, bootable clones, and encryption.
Type: Cloud-based Test Automation Platform
Founded: 2015
Primary Use: Web, mobile, and API testing
Supported Platforms: Web, iOS, Android, API