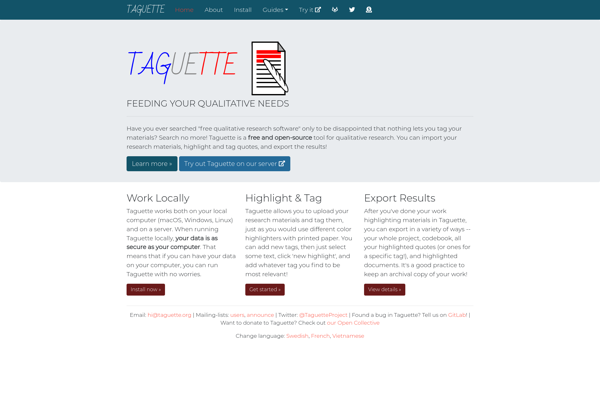
Description: Taguette is an open-source music tag editor for Windows, Mac, and Linux. It allows users to easily view and edit metadata tags of audio files, including artist name, album title, genre, year, track numbers, artwork, etc. With powerful batch processing, Taguette can automatically look up missing tags and fix errors in large music libraries.
Type: Open Source Test Automation Framework
Founded: 2011
Primary Use: Mobile app testing automation
Supported Platforms: iOS, Android, Windows
Description: MAXQDA is a qualitative data analysis software used for organizing, analyzing and visualizing textual, graphical and audio/video data. It allows importing data from interviews, focus groups, surveys, audio, videos, tweets, literature, webpages, images, PDFs and more. Key features include coding text, retrieving coded segments, visualizing connections in data, analyzing text with text mining tools, transcribing audio/video files, and team collaboration.
Type: Cloud-based Test Automation Platform
Founded: 2015
Primary Use: Web, mobile, and API testing
Supported Platforms: Web, iOS, Android, API