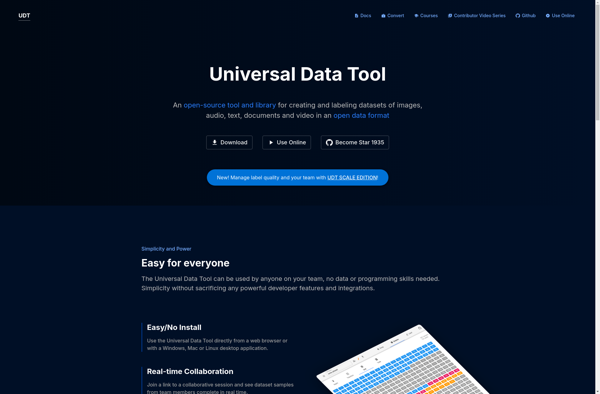
Description: UniversalDataTool is an open-source, cross-platform data visualization and analysis software. It allows importing, manipulating and graphing data from CSV, Excel, SQL databases and other sources. Key features include interactive charts, pivot tables, statistical analysis tools and Python scripting.
Type: Open Source Test Automation Framework
Founded: 2011
Primary Use: Mobile app testing automation
Supported Platforms: iOS, Android, Windows
Description: CVAT is an open source computer vision annotation tool for labeling images and video. It allows for collaborative annotation of datasets with features like predefined tags, interpolation of bounding boxes across frames, and review/acceptance workflows.
Type: Cloud-based Test Automation Platform
Founded: 2015
Primary Use: Web, mobile, and API testing
Supported Platforms: Web, iOS, Android, API