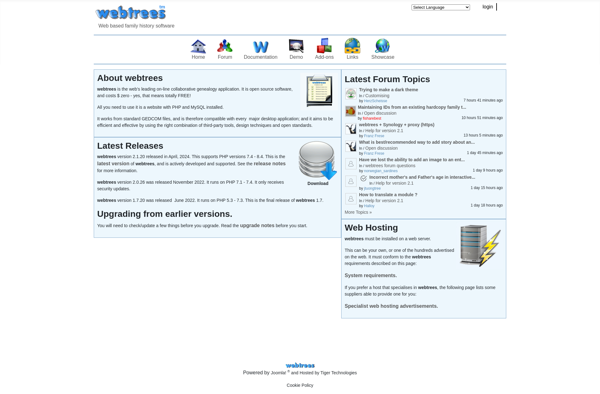
Description: webtrees is an open source web-based genealogy application used to track family histories and build family trees. It allows users to collaboratively build and share their family trees online.
Type: Open Source Test Automation Framework
Founded: 2011
Primary Use: Mobile app testing automation
Supported Platforms: iOS, Android, Windows
Description: Genealone is an open-source, desktop-based software tool for analyzing gene expression data from single-cell RNA sequencing experiments. It allows users to visualize, explore and interpret single-cell transcriptomic data through an interactive graphical user interface.
Type: Cloud-based Test Automation Platform
Founded: 2015
Primary Use: Web, mobile, and API testing
Supported Platforms: Web, iOS, Android, API