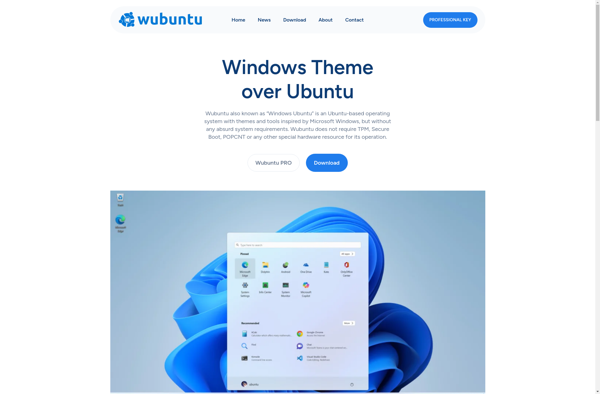
Description: Wubuntu is an open-source operating system based on Ubuntu Linux that aims to provide Windows compatibility and familiarity for users transitioning from Windows. It comes pre-installed with Wine and other tools to run Windows apps and has a user interface customized to resemble Windows.
Type: Open Source Test Automation Framework
Founded: 2011
Primary Use: Mobile app testing automation
Supported Platforms: iOS, Android, Windows
Description: Ubuntu Server is a free, open source operating system based on Linux, designed for servers, the cloud and large-scale deployments. It has a strong community and large ecosystem of compatible software and tools.
Type: Cloud-based Test Automation Platform
Founded: 2015
Primary Use: Web, mobile, and API testing
Supported Platforms: Web, iOS, Android, API