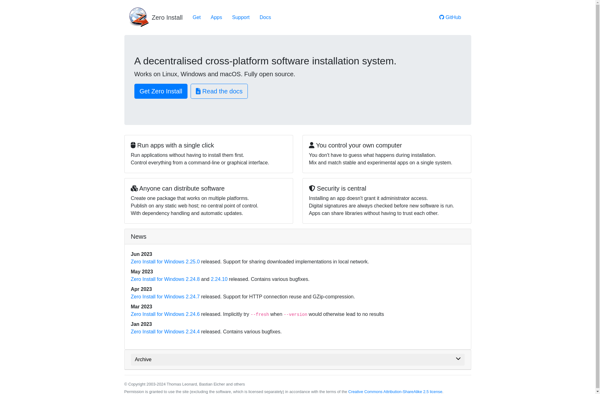
Description: Zero Install is a decentralized software distribution system that allows applications to be run directly from network resources without being installed locally. It aims to improve security and reduce installation issues.
Type: Open Source Test Automation Framework
Founded: 2011
Primary Use: Mobile app testing automation
Supported Platforms: iOS, Android, Windows
Description: UpdateStar is a software program that helps users keep other software up-to-date. It scans the computer for installed programs and checks if updates or patches are available from the vendors. It then allows the user to download and install those updates easily.
Type: Cloud-based Test Automation Platform
Founded: 2015
Primary Use: Web, mobile, and API testing
Supported Platforms: Web, iOS, Android, API