Add-apt-key
add-apt-key: Command Line Tool for Managing APT Repository Keys
A command line tool for Debian/Ubuntu Linux systems to add and remove trusted GPG keys used for authenticating and verifying software packages.
What is Add-apt-key?
The add-apt-key command in Linux is used to manage the list of trusted GPG keys used by the APT packaging system on Debian, Ubuntu, and related distributions. APT relies on these cryptographic keys to verify the authenticity and integrity of software packages downloaded from remote repositories.
When setting up custom APT repositories, whether for internal software or third-party applications, the repository maintainer generates a GPG key pair. The public key allows APT to ensure packages from that repository have not been tampered with. Before APT will trust packages signed with a key, you need to import the public key with add-apt-key.
Some common uses of the add-apt-key command include:
- Adding keys for third-party repositories not officially affiliated with your Linux distribution
- Importing keys for internal/private APT repositories in enterprise environments
- Updating expired repository keys that have been rotated by the maintainer
- Removing old keys that are no longer used to authenticate packages
The add-apt-key tool provides a simple command line interface for managing these trusted GPG keys instead of having to manually manipulate keyring files. An important security practice is to always verify keys with the developer/distributor before importing them on your system.
Add-apt-key Features
Features
- Adds, removes, and lists trusted GPG keys used for APT repository authentication
- Supports adding keys from a key server or a local file
- Provides a simple command-line interface for managing repository keys
- Helps ensure the integrity and security of software packages installed via APT
Pricing
- Open Source
Pros
Cons
Official Links
Reviews & Ratings
Login to ReviewThe Best Add-apt-key Alternatives
Top Os & Utilities and Package Management and other similar apps like Add-apt-key
Here are some alternatives to Add-apt-key:
Suggest an alternative ❐Y PPA Manager
Launchpad-getkeys
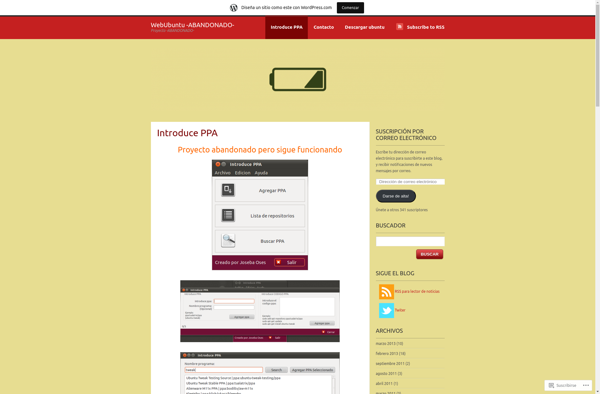
Introduce PPA