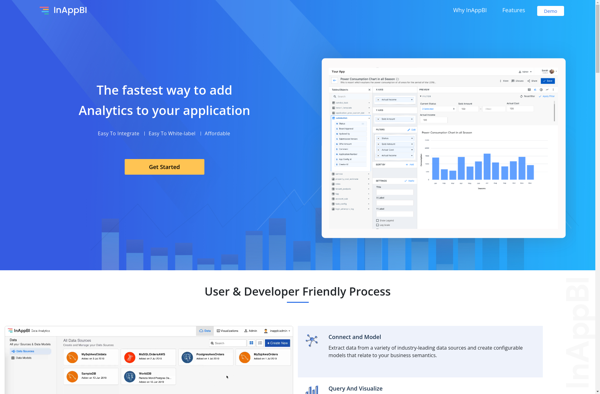
Description: InAppBI is a business intelligence and analytics platform designed for use within web and mobile applications. It allows developers to build custom analytics dashboards and reports that provide insights into app usage and customer behavior.
Type: Open Source Test Automation Framework
Founded: 2011
Primary Use: Mobile app testing automation
Supported Platforms: iOS, Android, Windows
Description: QueryTree is a data analytics tool that allows users to visually build SQL queries by dragging and dropping fields into a query tree interface. It eliminates the need to write SQL code manually.
Type: Cloud-based Test Automation Platform
Founded: 2015
Primary Use: Web, mobile, and API testing
Supported Platforms: Web, iOS, Android, API