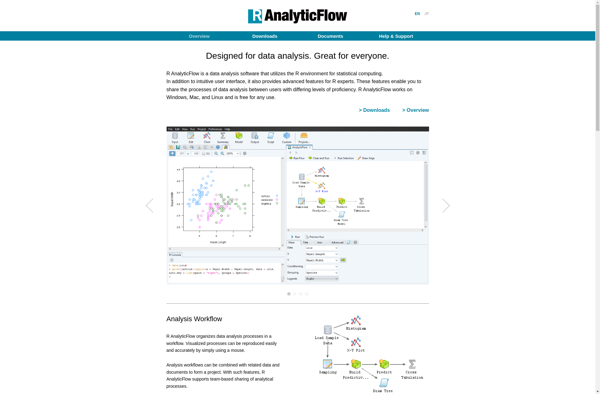
Description: R AnalyticFlow is an open-source data science platform for R that allows you to create reusable analysis flows and deploy them at scale. It has a code-free GUI for building flows visually as well as integration with Git for version control.
Type: Open Source Test Automation Framework
Founded: 2011
Primary Use: Mobile app testing automation
Supported Platforms: iOS, Android, Windows
Description: Dakota is an open-source software for design optimization, parameter estimation, uncertainty quantification, and sensitivity analysis. It interfaces with simulation codes written in C, C++, Fortran, Python, and MATLAB.
Type: Cloud-based Test Automation Platform
Founded: 2015
Primary Use: Web, mobile, and API testing
Supported Platforms: Web, iOS, Android, API