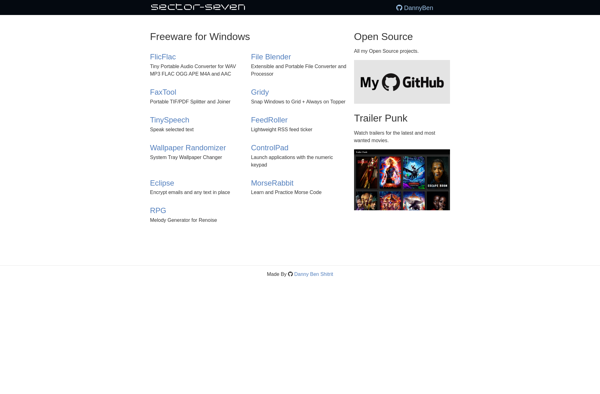
Window Manager
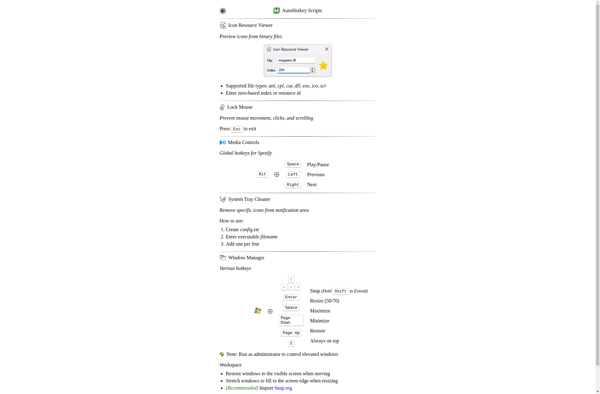
Window Manager: Manage Windows with Ease
A window manager is software that controls the placement and appearance of windows within a graphical user interface. It allows for basic window operations like opening, closing, resizing, moving windows.
What is Window Manager?
A window manager is a key piece of software in a graphical user interface that controls the placement and appearance of windows. It facilitates basic window operations like opening, closing, minimizing, maximizing, resizing, and moving windows around the screen.
The window manager plays an important role in managing how users interact with applications and providing a consistent user experience. It handles details like window borders and tittlebars, window stacking and layers, workspace management, special effects, and more.
Some common window managers used in Linux and other Unix-based operating systems include Mutter (GNOME), KWin (KDE Plasma), Xfwm (XFCE), Openbox, Fluxbox, Enlightenment, and many others. They offer varying degrees of customizability, resource usage, and integration with desktop environments.
Most modern operating systems have a built-in window manager like Windows Explorer on Windows, Finder on macOS, and the Android window manager on Android. Advanced users can replace these with third-party options for increased flexibility and efficiency in their workflows.
Window Manager Features
Features
- Manages the placement and appearance of application windows
- Allows for window operations like opening, closing, resizing, moving
- May provide titlebars, borders, controls for minimizing, maximizing, closing windows
- Controls how windows interact with each other
- May allow tiling or stacking of windows
- May provide virtual desktops to organize applications
Pricing
- Free
- Open Source
Pros
Cons
Reviews & Ratings
Login to ReviewThe Best Window Manager Alternatives
Top Os & Utilities and System Management and other similar apps like Window Manager
Here are some alternatives to Window Manager:
Suggest an alternative ❐MaxTo
Mosaico
FreeSnap
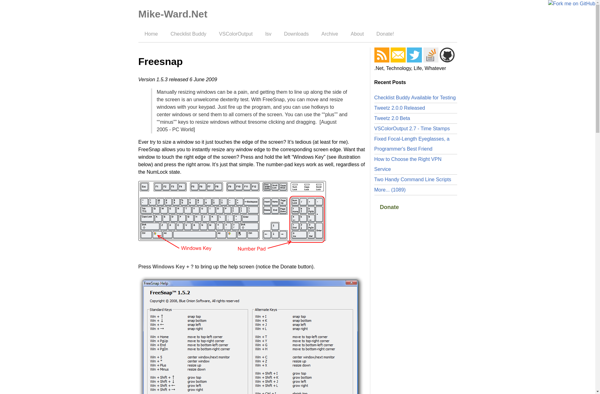
WindowSpace
GridMove
AllSnap

Stack WM
Gridy