Mastodon
Mastodon: Decentralized Social Media Platform
An open-source social media platform similar to Twitter, with a federated network of independently operated servers, allowing users to post 'toots' of up to 500 characters.
What is Mastodon?
Mastodon is an open-source, decentralized social networking platform launched in 2016. It operates as an alternative to commercial platforms like Twitter or Facebook by allowing a federated network of independently operated servers to exchange posts between one another.
Rather than having a single central authority like Twitter or Facebook, Mastodon servers can be operated by anyone with access to infrastructure who agrees to participate in the federation protocol. This lack of central control prevents a single entity from unilaterally changing policies or censoring users.
The user experience of Mastodon closely resembles Twitter, allowing short posts of up to 500 characters called 'toots' that can include media attachments. Users can follow other users not just on their home instance but across the entire federated network. Features like hashtags and content warnings for sensitive media function similarly as well.
A key reason for Mastodon's creation was dissatisfaction over the proliferation of hate speech, harassment, and lack of chronological timelines on commercial social media platforms. By making moderation responsibilities decentralized rather than centralized in the hands of a single corporation, Mastodon offers an alternative model for social media governance and policy.
Mastodon Features
Features
- Decentralized social network - no single company/server owns the network
- Open source codebase allows anyone to run a server
- Federated timeline shows posts from all servers you follow
- Granular privacy controls for posts - public, followers-only, etc
- Media attachments like images and videos
- Short post limit compared to other platforms
- Chronological timeline with no algorithmic sorting
Pricing
- Open Source
Pros
Cons
Official Links
Reviews & Ratings
Login to ReviewThe Best Mastodon Alternatives
Top Social & Communications and Microblogging and other similar apps like Mastodon
Tumblr
Gab
Twell.me
MeWe

SpaceHey
Efimero
Google Plus
D.Buzz
Minds
Toko
THINK thenlive
Diaspora
KOUHMAN
Chttr.co
Micro.blog
Post News

Pixelfed
ZeroMe
MediaRevolt
Phanpy
Hawaar
App.net
Drixr
Bluesky
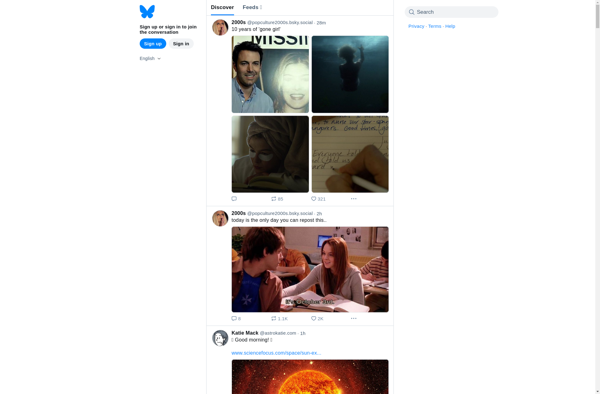
Fandomers
Micrro
Mumblit
YouWeb
Woddal
Bastyon
Pebble.is
Posthaven
Flote
StatusNet
Tally App
Pleroma

Alloblak

Truth Social
Parler

GNU social
Hive Social
Misskey
Community Builder
PenPal World

ColdCast

Baaz
Cohost
Chaino
Movim
Hylo
Dinky Social Network
Apsense
Manyverse
ADZbuzz
Mirror Island
SocialPage
FineFriends

OVBE.Club
Thoughtifies
Kaana
Kizie

GoToSocial
Human Connection

Scuttlebutt.nz

My World Network
Social Home
Quizana
Total Social
Communecter
Anancus
Tribyo
NewTimeBox
Friend Xone
CYGO Network
Kaverti
Pixeljab
SocialNumber
Kocpit
E-Sathi
Gymmr

Soapbox.pub
The Social Network
PostActiv