Windows Task Manager
Windows Task Manager: System Monitor for Microsoft Windows
Windows Task Manager is a system monitor program included in Microsoft Windows that provides users with information about computer performance and running applications. It allows users to view CPU and memory usage, kill unresponsive programs, and adjust the priority of running processes.
What is Windows Task Manager?
Windows Task Manager is a system monitor, process manager, and startup manager included with Microsoft Windows that provides users with detailed information about their computer's performance and running applications, as well as control over processes and the ability to adjust parameters. First introduced as Windows NT Task Manager in Windows NT 4.0, it was renamed to Windows Task Manager in Windows XP.
When opened, Windows Task Manager shows CPU and memory usage graphs, statistics for these resources, total system uptime, and a list of currently running processes. For each process, it shows memory and CPU usage, the account it's running under, and a description. From the Processes tab, users can end non-responding applications, change process priority to adjust resource allocation, and open the process location in File Explorer. There are also tabs for performance monitoring graphs, startup applications, users logged in, and network connections.
Key features of Windows Task Manager include:
- View real-time graphs and history of CPU, memory, disk, and network usage
- See which processes and applications are using the most system resources
- Stop crashed, frozen, or unresponsive apps
- Change process priority levels to reallocate CPU and memory resources
- Monitor system uptime and CPU speeds
- Control which applications run at startup
- View and end user sessions over Remote Desktop
- See incoming and outgoing network connections
With detailed statistics and control over running processes, Windows Task Manager provides vital tools for monitoring system health, troubleshooting performance issues, stopping unresponsive apps, and managing how applications utilize resources.
Windows Task Manager Features
Features
- View running processes
- View CPU and memory usage
- Kill unresponsive programs
- Adjust process priority
- View network usage
- View disk usage
- View GPU usage
- View startup programs
- View Windows services
Pricing
- Free
Pros
Cons
Reviews & Ratings
Login to ReviewThe Best Windows Task Manager Alternatives
Top Os & Utilities and System Monitoring and other similar apps like Windows Task Manager
Here are some alternatives to Windows Task Manager:
Suggest an alternative ❐Htop
Process Hacker
AMD Link
Stacer
Process Lasso
LikeTaskManager
Vtop
TaskExplorer
StatusPilatus
Resource Monitor
Venmon
MiTeC Task Manager Deluxe
Glances
Atmonitor
Xfce Task Manager
KSysGuard
Remote Process Explorer

SpyStudio
System Informer
AnVir Task Manager
Kiwi application monitor

LXTask

KillSwitch
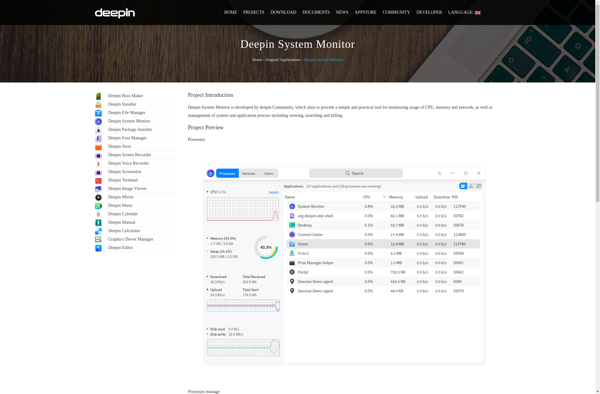
Deepin System Monitor
Free Extended Task Manager
Security Task Manager
MATE System Monitor
DBCTaskman
MyProcesses
Alternate Task Manager

Security Process Explorer
ES Task Manager
NotCPUCores
SterJo Task Manager
DTaskManager
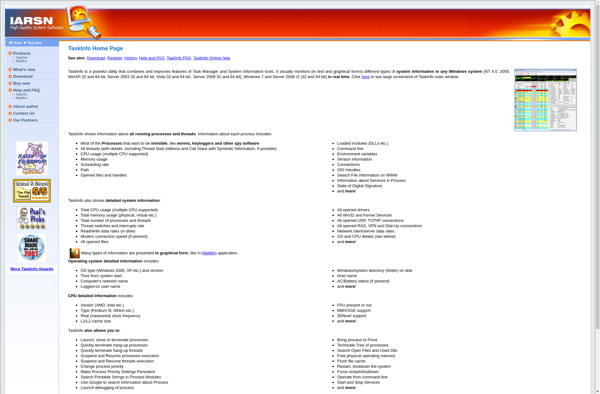
TaskInfo
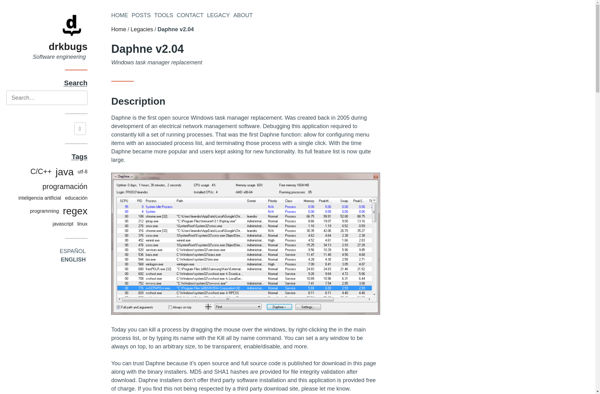
Daphne
Process Scanner
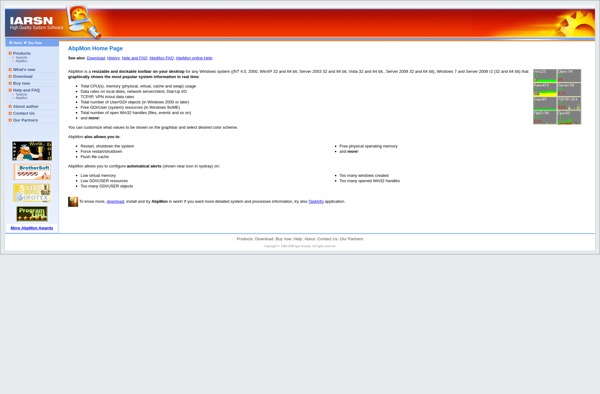
AbpMon
Tasks Explorer
MagicanLite
Process History
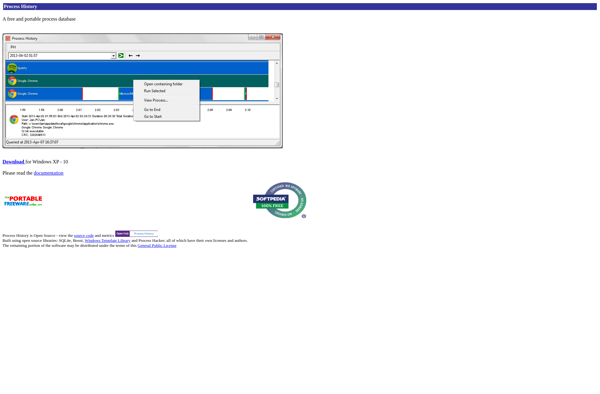
RemoteProcessExplorer

Auslogics Task Manager
